DUTCH Cycle Mapping™
The DUTCH Cycle Mapping™ maps the progesterone and estrogen pattern throughout the menstrual cycle. It provides the full picture of a woman’s cycle to answer important questions for patients with month-long symptoms, infertility, and PCOS. Nine (9) targeted estrogen and progesterone measurements are taken throughout the cycle to characterize the follicular, ovulatory, and luteal phases.
What is DUTCH Cycle Mapping™?
For some women, testing reproductive hormones (progesterone, estrogen, etc.) on a single day is sufficient. In other scenarios, the clinical picture cannot be properly captured without “mapping” out the hormonal pattern throughout their menstrual cycle.
The expected pattern of hormones shows relatively low estrogen levels early in the cycle, a surge around ovulation and modest levels in the latter third of the cycle (the luteal phase). Progesterone levels, on the other hand, stay relatively low until after ovulation. After ovulation, levels ideally increase (>10-fold) and then drop back down at the end of the cycle. A disruption in this cycle can lead to infertility or hormonal imbalance.
WHEN IS DUTCH CYCLE MAPPING™ RECOMMENDED?
• Women struggling with infertility
• Women with cycling hormones and no menses
• Partial hysterectomy (ovaries intact but no uterus)
• Ablations
• Women with irregular cycles
• PCOS
• If the luteal phase shifts from month-to-month
• Not sure when to test due to long or short cycles
• Women whose hormonal symptoms tend to fluctuate throughout the cycle
• PMS, mid-cycle spotting, migraines, etc.
WHEN IS DUTCH CYCLE MAPPING™ NOT NEEDED? (DUTCH COMPLETE™ IS SUFFICIENT)
• Postmenopausal women
• Women on birth control
• Women with cycles that follow the expected pattern


Most Convenient Method for Month-Long Analysis
EASY SAMPLE COLLECTIONS MAKE FOR BETTER TESTING
Salivary mapping of hormones limits the number of collections, which may result in missing progesterone, and especially estrogen peaks if not timed correctly. For women with irregular cycles, this is particularly problematic. DUTCH Cycle Mapping™ uses more sample collections (convenient, first-morning urine collections) and performs testing on targeted samples based on the actual length of the cycle. This allows for better characterization of both the ovulatory and luteal peaks
BETTER TESTING MAKES FOR BETTER TREATMENT
Treating women appropriately and effectively with irregular cycles, fertility problems, or who have had an ablation can be challenging to practitioners because it is difficult to fully ascertain what their hormones are doing and when. By using the DUTCH Cycle Mapping™ test, a complete picture of the patient’s cycle in graph format will allow for a more accurate and comprehensive treatment program specific to the patient’s situation. The clinician can understand if and when a patient is ovulating. They can also determine why their patients are having mid-cycle spotting or hormonal migraines. This will help them get a clear understanding of how their patient’s ovaries are functioning or look further into fertility issues. These answers will help with the clinician’s goal of individualized medicine.
HOW WELL DO ESTROGEN AND PROGESTERONE VALUES CORRELATE WITH SERUM MEASUREMENTS?
Hormone patterns throughout the menstrual cycle parallel simultaneously collected serum samples very well. When compared to salivary measurements, DUTCH measurements showed improved correlation to serum for both progesterone and especially for estradiol.
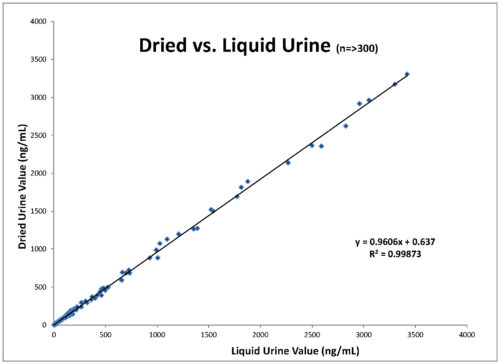
DO DRIED SAMPLES COMPROMISE THE ANALYSIS?
Dried samples are accurate for hormone testing, and values correlate to liquid samples (see graph, below). Samples are more stable once they are dried and also much easier to store and ship than liquid samples.
METHODS USED FOR TESTING
Estrogen and progesterone metabolites for this profile are all tested (9x) by LC-MS/MS. This is the most sensitive and accurate method for testing urinary reproductive hormones and their metabolites. Other options include immunoassays, GC-MS, or GC-MS/MS






